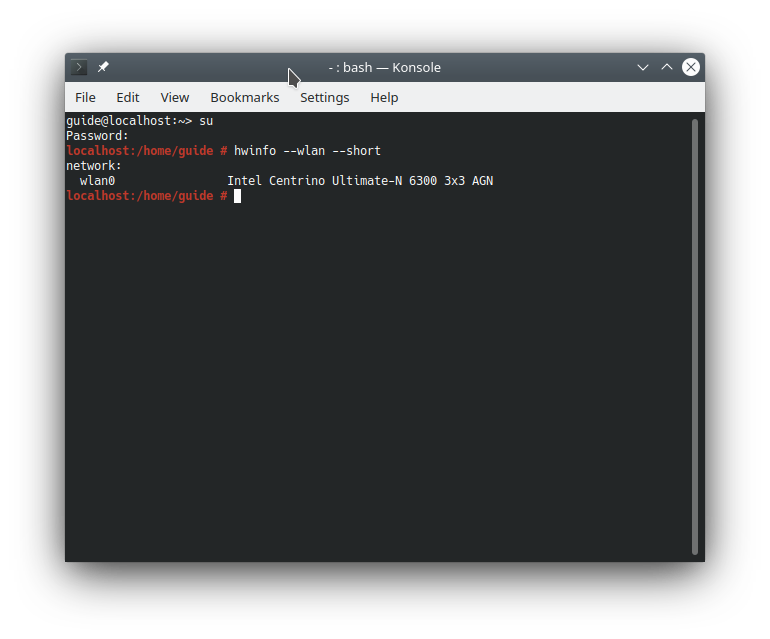
Configurar Wifi Centos 6 Download
May 23, 2013 This is a guide on configuring network in CentOS 6.x in Virtual Box with screenshots (using terminal).[UPDATE: This guide can also be used to configure network on CentOS 6.5]So, here I have used CentOS 6.3 minimal and will be discussing on configuring the Virtual Box and CentOS for network access. If you need help installing CentOS.
I'm migrating from an openSUSE (12.x) CLI home office server to CentOS 6.3. Claviculas de salomao pdf download. I can install the CLI CentOS 6.3 fine, but then how do I connect that to my home wifi?
There is a 'Configure network' button during the anaconda graphical install, and it has options for wifi, but even setting the wifi here results in no connection when the install finishes and I log into the CLI. OpenSUSE has Yast (even for CLI!) where you could configure anything and everything. I see a few system-config-* type commands on CentOS but nothing where I input my wifi SSID and passkey. Does anybody know which files I need to edit or which commands I need to run to get my CentOS laptop home office server to connect - on boot - to my home wifi?
 Thanks a lot. Does anybody know what the difference is with the different install types on CentOS 6.3?
Thanks a lot. Does anybody know what the difference is with the different install types on CentOS 6.3?
They've got 'basic server', 'web server', 'minimal desktop' and a few more.
By default Centos 6 new installation will not have network access, which means you need to configure ip address to the network interfaces by yourself. In this article we can see how to setup network in centos 6, i.e. Assigning ipaddress in static and in DHCP mode. » DHCP mode: Assigning ip address in DHCP mode Step 1 » Check the network interface name by typing below command [root@leela ~]# ip a 1: lo: mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo inet6::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: p4p1: mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000 link/ether 00:22:19:09:4d:3c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff Here “lo” is the loopback interface and “ p4p1” is the network interface that you need to configure.
Step 2 » you can see the file named ifcfg-p4p1 ( Interface name ) in the location “ /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/”, open the file and you can see the lines as below. BOOTPROTO = 'dhcp' #Assigning IP from DHCP Step 3 » Start the network service and you can see the status as below. [root@leela ~]# service network start Bringing up loopback interface: [ OK ] Bringing up interface p4p1: Determining IP information for p4p1. [ OK ] Step 4 » Now you can see the ip address “192.168.1.12” assigned to the interface p4p1 using dhcp. DNS2 = 4.2.2.2 #Secondary DNS Step 3 » Start the network service and you can see the status as below. [root@leela ~]# service network start Bringing up loopback interface: [ OK ] Bringing up interface p4p1: [ OK ] Step 4 » Now you see the ip address “192.168.1.12” assigned to the interface p4p1.
[root@leela ~]# ip a 1: lo: mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo inet6::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: p4p1: mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000 link/ether 00:22:19:09:4d:3c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.12/26 brd 172.27.6.63 scope global p4p1 inet6 fe80::222:19ff:fe09:4b3c/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever Also see.